The liver is one of the most important organs in the body, responsible for a variety of functions essential for overall health. From detoxifying harmful substances to metabolizing nutrients, the liver plays a key role in maintaining a healthy system.
As individuals look for natural ways to improve liver health, one question that often arises is whether magnesium can aid in detoxifying the liver.

Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays numerous roles in the body, from supporting muscle function to maintaining bone health and regulating blood sugar levels.
But can it also support the liver’s detoxification processes? This blog post will dive into the relationship between magnesium and liver health, explore its potential detoxifying effects, and provide insight into how you can incorporate magnesium into your routine for better liver function.
Understanding the Liver’s Detoxification Process
Before delving into magnesium’s potential role in detoxifying the liver, it’s essential to understand the liver’s natural detoxification process. The liver detoxifies the body in two main phases:
-
Phase 1 Detoxification: This phase involves the breakdown of toxins by liver enzymes. These enzymes work to convert fat-soluble toxins into less harmful substances, making them easier for the body to eliminate. This process can generate free radicals, which may cause oxidative stress in the liver cells if not neutralized.
-
Phase 2 Detoxification: In this phase, the substances created in Phase 1 are further processed and conjugated with molecules that make them water-soluble. This makes the toxins easier for the body to eliminate through urine or bile. Antioxidants play a vital role in this phase by neutralizing free radicals and minimizing oxidative damage.
The liver is naturally equipped to handle a wide range of substances, from alcohol and medications to environmental toxins and processed foods.
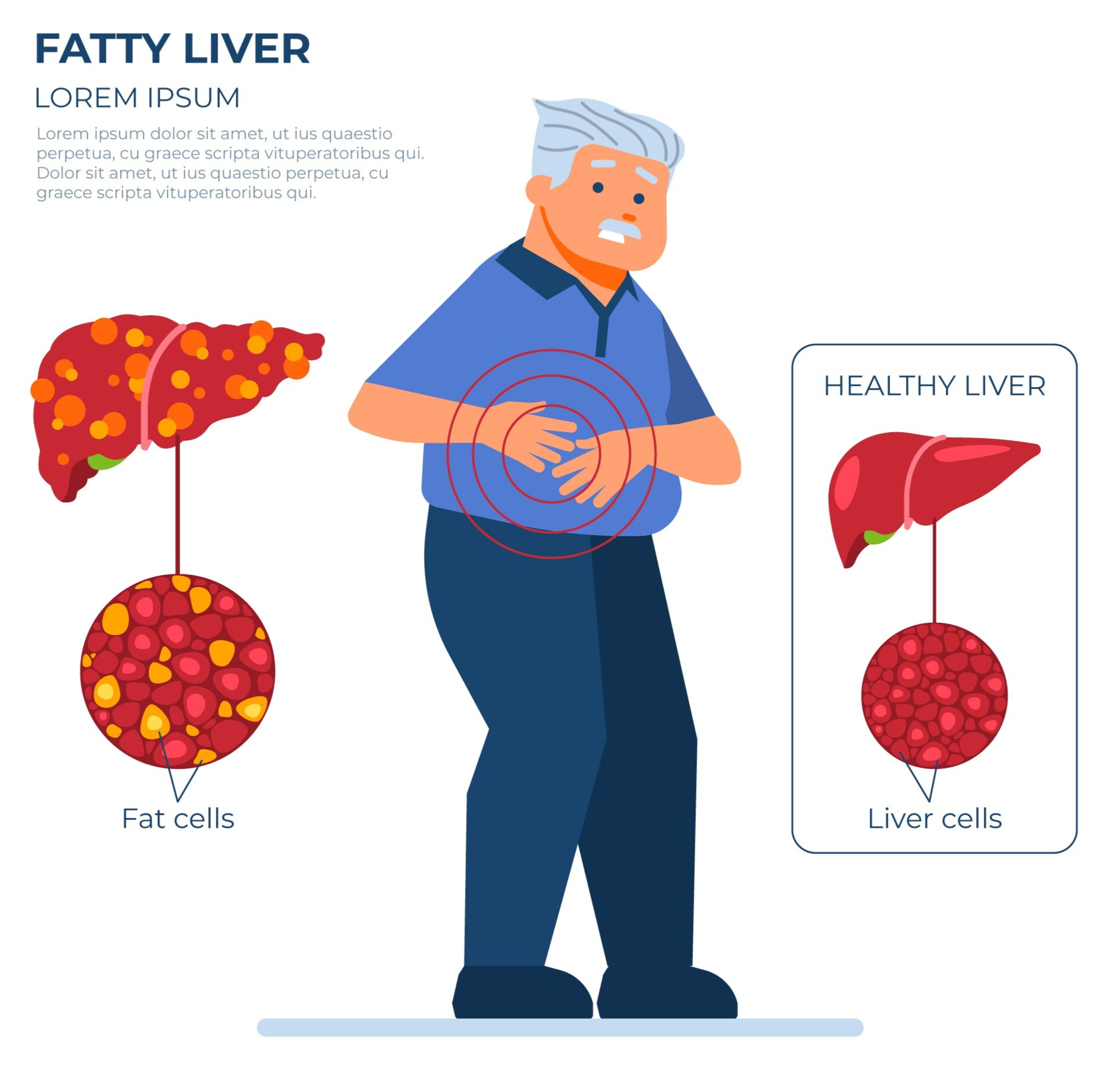
However, over time, an accumulation of these toxins and an imbalance in liver function can lead to a variety of health issues, including fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer.
Magnesium and Liver Health
Magnesium is a mineral that is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including energy production, DNA repair, and muscle function. Studies have shown that magnesium is also crucial for maintaining healthy liver function. It is believed that magnesium can help to:
-
Regulate Inflammation: Magnesium has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the liver. Chronic inflammation is one of the leading causes of liver disease, including fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
-
Support Antioxidant Activity: Magnesium is a cofactor for several antioxidant enzymes in the body. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals generated during the detoxification process, thus protecting the liver from oxidative stress. This is important because oxidative stress can contribute to liver damage and the progression of liver diseases.
-
Enhance Liver Enzyme Function: Magnesium is involved in the activation of key enzymes responsible for detoxification in the liver. By supporting these enzymes, magnesium can enhance the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances.
-
Aid in Bile Production: Magnesium is thought to help with the production and flow of bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver that helps break down fats. Healthy bile flow ensures proper digestion and supports the liver in its detoxification processes.
Can Magnesium Detoxify the Liver?
Now that we have a clearer understanding of magnesium’s role in liver health, let’s explore the question at hand: Can magnesium detoxify the liver?
The short answer is that magnesium may support liver detoxification, but it is not a magic bullet or an immediate solution for liver cleansing.
Instead, magnesium works synergistically with the liver’s natural detoxification processes, supporting the enzymes and antioxidants needed to help the liver function optimally.
Magnesium and Phase 1 Detoxification
As mentioned earlier, Phase 1 detoxification involves breaking down toxins, often creating free radicals in the process. Magnesium supports the activity of enzymes involved in this phase, helping to break down toxins more efficiently and neutralize harmful free radicals.
By reducing oxidative stress, magnesium helps ensure that Phase 1 detoxification doesn’t cause damage to liver cells.
Magnesium and Phase 2 Detoxification
In Phase 2, the liver further processes toxins by conjugating them with water-soluble molecules, which facilitates their elimination.
Magnesium is involved in various reactions that enhance this process, including the synthesis of certain conjugating molecules, such as glutathione. Glutathione is one of the body’s most powerful antioxidants and plays a crucial role in the liver’s detoxification abilities.
Moreover, magnesium has been shown to reduce the risk of oxidative damage to the liver and other organs, helping to protect the liver from further harm during the detoxification process. By supporting Phase 2 detoxification, magnesium ensures that toxins are safely processed and eliminated from the body.
Magnesium and Liver Diseases
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to various liver diseases, including fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver fibrosis. Studies have shown that people with low magnesium levels may be at a higher risk for these conditions, suggesting that magnesium plays a protective role in liver health.
By promoting liver cell health, reducing inflammation, and supporting detoxification, magnesium may help prevent or mitigate the damage caused by these diseases.
How to Incorporate Magnesium for Liver Detoxification
Magnesium is essential for overall health, and if you are looking to support your liver health, there are several ways you can incorporate magnesium into your routine.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium
One of the best ways to boost your magnesium levels is by consuming magnesium-rich foods. Some excellent sources of magnesium include:
-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are high in magnesium.
-
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are great options.
-
Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats provide a significant amount of magnesium.
-
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in magnesium.
-
Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel provide magnesium, along with other important nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids.
Magnesium Supplements
- If you find it difficult to get enough magnesium from food alone, supplements can be a good option. Magnesium supplements come in several forms, including magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide, and magnesium glycinate.
- The type of magnesium supplement you choose may affect its absorption and how gentle it is on your digestive system. For optimal liver health, magnesium glycinate is often recommended due to its high bioavailability and gentle effect on the stomach.
Topical Magnesium
- Magnesium oil and magnesium creams are other options for increasing your magnesium levels. These products can be applied directly to the skin, where the magnesium is absorbed through the dermis.
- While there is limited research on the effectiveness of transdermal magnesium absorption, many people report positive results from using magnesium topically for muscle relaxation and general well-being.
Magnesium-Rich Bath
- Taking a bath with Epsom salts, which contain magnesium sulfate, is a relaxing and rejuvenating way to increase magnesium levels.
- The magnesium can be absorbed through the skin while you relax in the warm water. This can help reduce muscle soreness, alleviate stress, and support overall detoxification.
Other Liver-Boosting Practices
In addition to incorporating magnesium into your routine, there are several other practices that can help detoxify the liver and improve overall liver function:
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports kidney function and helps the liver flush out toxins more effectively.
-
Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients that support liver health.
-
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves circulation and helps the liver process and eliminate toxins.
-
Avoid Alcohol and Toxins: Excessive alcohol consumption and exposure to environmental toxins can damage the liver. Limiting your exposure to these substances will help your liver function more efficiently.
Conclusion
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, and its potential benefits for liver health are significant.
While magnesium itself may not act as a standalone detoxifier for the liver, it supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes by enhancing enzyme activity, reducing inflammation, and protecting against oxidative stress.
If you’re looking to support your liver health, incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet or considering magnesium supplements could be an excellent option.
Along with a healthy lifestyle, magnesium can help optimize liver function and support your body’s ability to detoxify effectively.
References
Magnesium and Liver Health: A Review of Potential Benefits: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7273690/
The Role of Magnesium in the Prevention and Treatment of Liver Diseases: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31390421/
Magnesium Deficiency and Liver Disease: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5855205/
Magnesium Supplementation for Liver Health: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31915577/